Catalog
Tags

10 CNC Drill Geometries Every Machinist Must Know
TL;DR: The right CNC drill geometry significantly impacts tool life, chip evacuation, and surface finish. The 10 essential geometries include twist drills, center drills, spot drills, peck drills, and more – each designed for specific materials and operations.
How CNC Drill Geometry Works
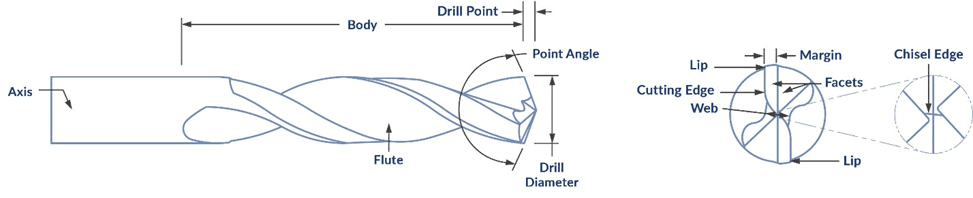
Drill geometry refers to the specific angles, shapes, and features of a cutting tool that determine its performance characteristics. The three fundamental elements are:
- Point Angle (118° standard, 135° for harder materials)
- Helix Angle (affects chip evacuation)
- Lip Relief Angle (prevents rubbing)
The 10 Essential CNC Drill Geometries
| Geometry Type | Best For | Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Twist Drill | General purpose drilling | Steel, Aluminum, Plastics |
| High Helix Drill | Soft materials | Aluminum, Copper, Plastics |
| Low Helix Drill | Hard materials | Stainless Steel, Titanium |
| Spot Drill | Creating starter holes | All materials |
| Center Drill | Lathe work, precise centering | All materials |
| Peck Drill | Deep hole drilling | All materials |
| Step Drill | Multiple diameters | Thin materials |
| Indexable Drill | High production | Steel, Cast Iron |
| Gun Drill | Extreme depth-to-diameter | All materials |
| Flat Bottom Drill | Bottom finishing | All materials |
Advantages and Applications
- Standard Twist: Most economical, general purpose
- High Helix: Superior chip evacuation in gummy materials
- Low Helix: Increased rigidity for hard metals
- Indexable: Cost-effective for high-volume production
- Gun Drills: Essential for deep hole drilling (10x diameter+)
Real-World Applications
Aerospace Case Study: Boeing reduced titanium drilling costs by 22% by switching from standard twist drills to low-helix carbide drills with 135° point angles, extending tool life by 3x.
Automotive Example: Ford uses indexable insert drills for engine block production, achieving 500+ holes per insert in cast iron.
CNC Drill Geometry FAQ
- Q: When should I use a spot drill vs center drill?
A: Spot drills for CNC mills (better concentricity), center drills for lathes - Q: What’s the best drill geometry for aluminum?
A: High helix (35-45°) with polished flutes and 130-140° point angle - Q: How often should I check drill geometry?
A: Inspect after each major job or every 50-100 holes for critical applications
Upgrade Your Drilling Performance
Ready to optimize your CNC drilling operations? Download our free drill geometry selection guide or schedule a tooling consultation with our machining experts today.
Pro Tip: Always match your drill geometry to both material and machine rigidity – a perfect geometry in specs won’t perform if your setup can’t handle the cutting forces.
Need Precision CNC Machining for Your Mold Components?
We specialize in custom CNC machining of mold inserts, slide cores, ejector plates, mold bases, and lifters
all made to your exact drawings and specifications.
👉 Let’s Build Your Next Project Together!
Tell us your needs and upload your drawings — we’ll get back within 24 hours.